分类的原理 对于分类的作用恐怕大家都是知道的吧,今天就让我们一起研究一下分类的实现原理。
首先创建一个person类,然后在创建person类的两个分类Person+eat&Person+Run。
1、生成c++文件,查看c++文件中的实现
2、如果c++文件中实现介绍的不太具体就去查看源码 实现
我们使用xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc Person+eat.m来生成c++代码
我们可以找到分类都包含了哪些东西
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 struct _category_t { const char *name; struct _class_t *cls ; const struct _method_list_t *instance_methods ; const struct _method_list_t *class_methods ; const struct _protocol_list_t *protocols ; const struct _prop_list_t *properties ; };
我们发现里面并没有对方法属性协议等等的具体实现过程,那么我们在去源码 中查看一下相关实现过程。
源码解读顺序
1、objc-os.mm(runtime初始化的代码)
_objc_init
map_images
map_images_nolock
2、objc-runtime-new.mm
_read_images
remethodizeClass
attachCategories
attachLists
realloc、memmove、 memcpy
我们按照源码查找一路找到attachCategories方法,我们发现这个方法就是对分类的实现。里面第一句解释Attach method lists and properties and protocols from categories to a class.将方法列表、属性和协议从类别附加到类中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 static void attachCategories(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flush_caches) { if (!cats) return ; if (PrintReplacedMethods) printReplacements(cls, cats); bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass(); method_list_t **mlists = (method_list_t **) malloc (cats->count * sizeof (*mlists)); property_list_t **proplists = (property_list_t **) malloc (cats->count * sizeof (*proplists)); protocol_list_t **protolists = (protocol_list_t **) malloc (cats->count * sizeof (*protolists)); int mcount = 0 ; int propcount = 0 ; int protocount = 0 ; int i = cats->count; bool fromBundle = NO; while (i--) { auto & entry = cats->list [i]; method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta); if (mlist) { mlists[mcount++] = mlist; fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle(); } property_list_t *proplist = entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi); if (proplist) { proplists[propcount++] = proplist; } protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocols; if (protolist) { protolists[protocount++] = protolist; } } auto rw = cls->data(); prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle); rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount); free (mlists); if (flush_caches && mcount > 0 ) flushCaches(cls); rw->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount); free (proplists); rw->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount); free (protolists); }
我们发现rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);方法是实现将所有分类的对象方法,附加到类对象的方法列表中,其他两个属性和协议都是调用这个方法,我们分析一个就可以了。
点击进入attachLists方法,里面有一段实现代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 if (hasArray()) { uint32_t oldCount = array ()->count; uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount; setArray((array_t *)realloc (array (), array_t ::byteSize(newCount))); array ()->count = newCount; memmove(array ()->lists + addedCount, array ()->lists, oldCount * sizeof (array ()->lists[0 ])); memcpy (array ()->lists, addedLists, addedCount * sizeof (array ()->lists[0 ])); }
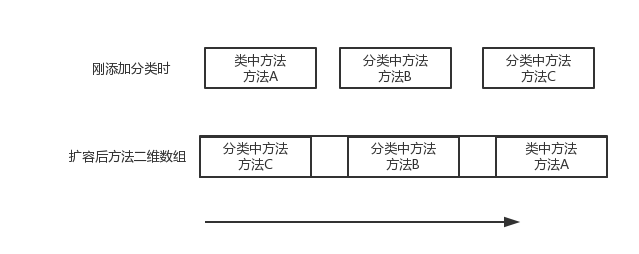
1、扩容,把类中的方法数组和分类中的方法数组计算出来
2、memmove把类中方法放到数组的最后一位
3、memcpy把分类中的方法放到数组的前面。